Published : 2025-09-23
On September 23, 1969, China successfully conducted its first underground nuclear test.
In the 1960s, the United States, the Soviet Union, and Britain signed the "Partial Test Ban Treaty" (PTBT).
It was seen as a means to cement their monopoly on nuclear power and to prevent other countries from conducting nuclear tests and developing nuclear weapons.
To break this monopoly, China quietly established the underground nuclear test research group and successively began the selection of underground nuclear test sites, laboratory simulations, and studies on the effects of explosions.
From project preparation to technical argumentation and engineering construction, it took nearly five years for the entire team to successfully establish a comprehensive testing and full command and control system for underground nuclear tests. The prep work was completed.
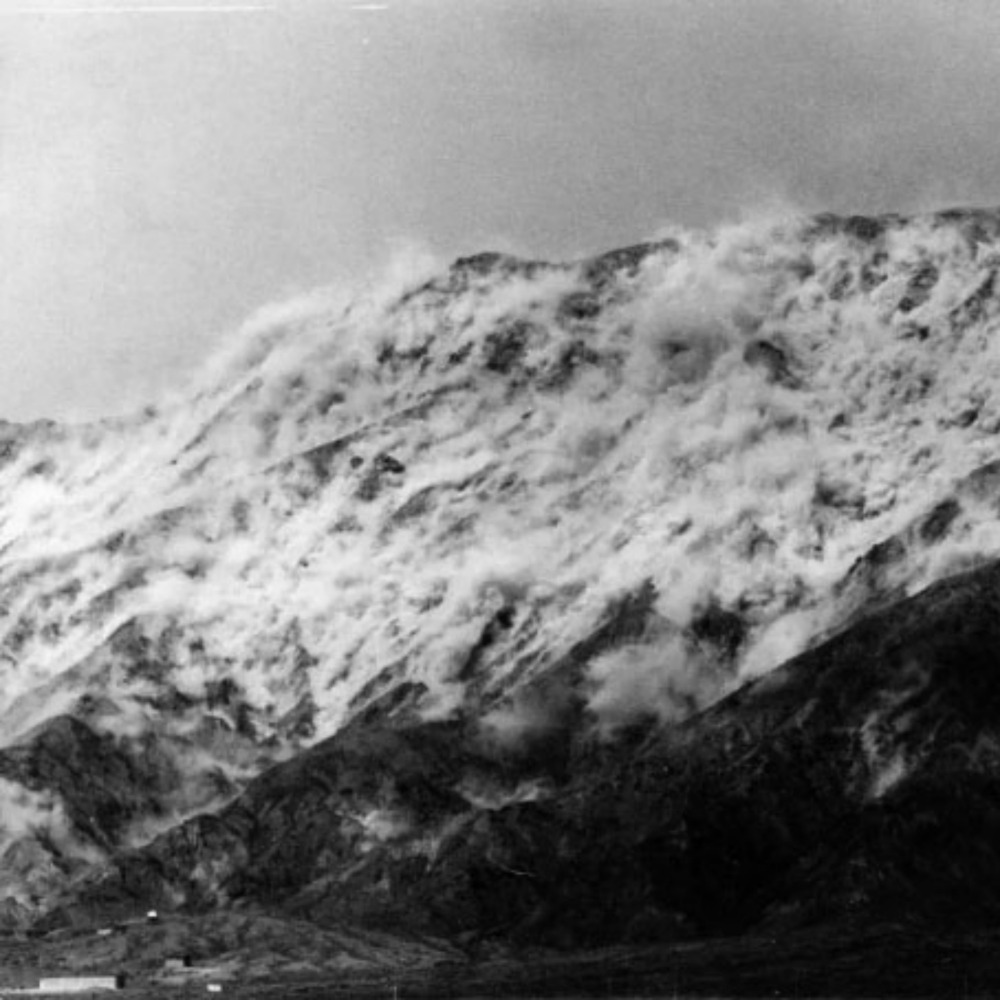
At 15 minutes past midnight on that day, the underground nuclear test was initiated.
The earth-shattering explosion released a massive amount of energy, causing the mountain in the test area to shake violently.
China's first underground nuclear test involved digging a specially designed long tunnel in the mountain, then placing a nuclear device and various detectors inside the tunnel, which was finally backfilled and sealed according to a special plan.
After the test, the tunnel was self-sealed, with no "roof fall" (i.e., natural collapse of the rock layer) or fail, and the explosive power of the nuclear device essentially met the design requirements.