Published : 2025-01-03
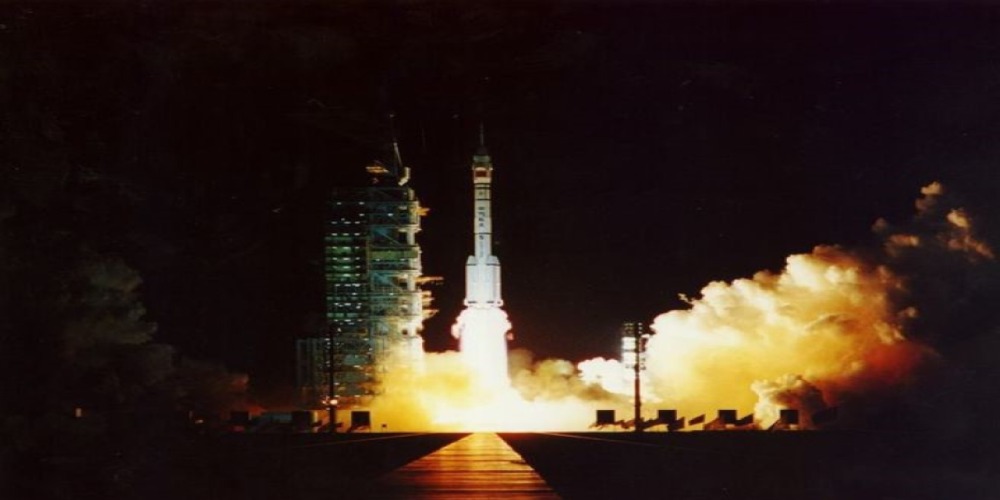
On January 3, 2019, China's Chang'e-4 spacecraft successfully landed on the far side of the Moon.
Chang'e-4 was launched in the early hours of December 8, 2018, and entered lunar orbit smoothly four days later.
On December 30, it successfully executed an orbital manoeuvre on the lunar orbit, entering the predetermined landing preparation orbit on the far side of the Moon.
At 10:15 am on January 3, Beijing Aerospace Control Centre (BACC) sent a command for Chang'e-4 to start its descent from a distance of 15 kilometres above the lunar surface.
Engines were ignited to gradually decrease the speed from 1.7 km/s to zero relative to the Moon.
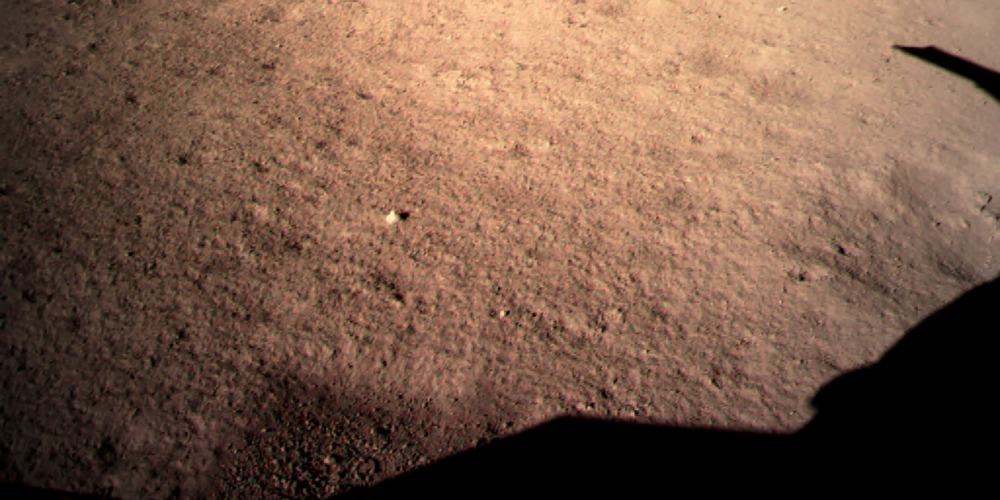
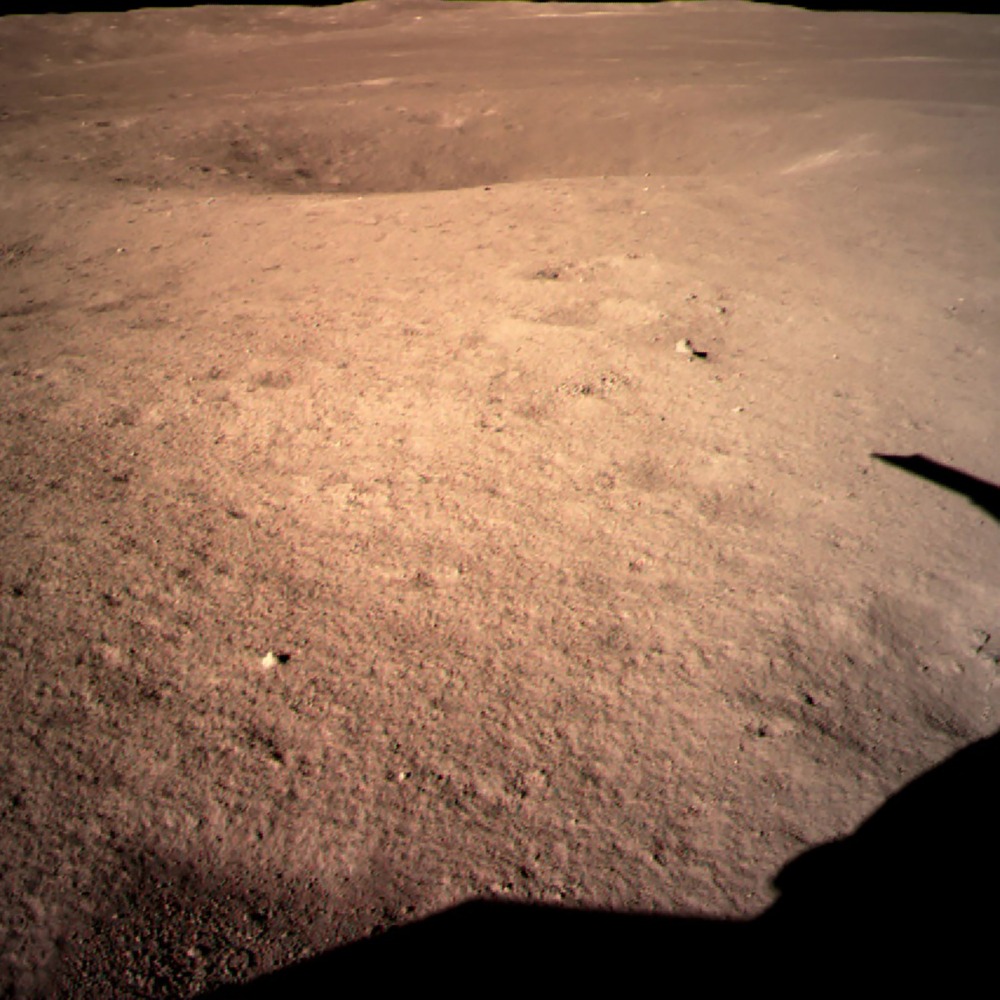
After performing rapid attitude adjustments, hovering, and other manoeuvres, Chang'e-4 made a slow vertical descent and autonomously landed inside the Von Kármán crater in the South Pole-Aitken Basin on the far side of the Moon.
After landing, Chang'e-4 immediately transmitted the first close-up image of the far side of the Moon through the Queqiao relay satellite.
Chang'e-4 achieved the first soft landing of a human probe on the far side of the Moon and the first relay communication between the far side of the Moon and Earth.