Published : 2025-04-05
April 5, 1952, marked the full commencement of the first phase of China's Jingjiang flood diversion project.
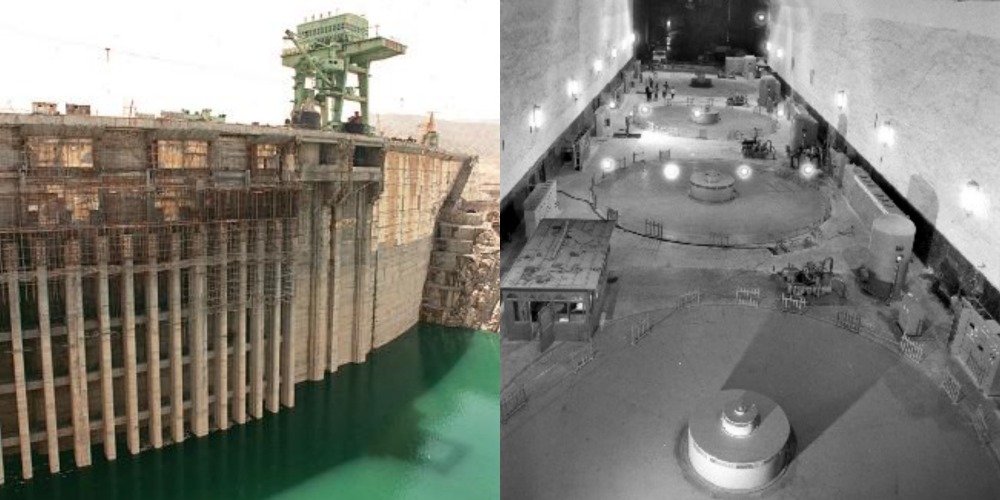
The Jingjiang flood diversion project was the first large-scale water conservancy project for the management and development of the Yangtze River and also the first major water conservancy project after the founding of New China.
Its primary purpose is to safeguard the lives and property of people in Hubei Province and Hunan Province.
The 77-km long section of Yangtze River from Zhicheng in Hubei to Chenglingji in Hunan that crosses the two provinces, is called Jingjiang (荊江).
In the past, the Yangtze River often experienced floods, and the two banks of Jingjiang, being low-lying areas, were the most frequently and severely affected sections.
Therefore, managing Jingjiang became a primary task for managing the Yangtze River after the founding of New China.
According to statistics, over 300 years before 1949, the main dikes of Jingjiang breached 34 times.
In modern times, there was an average of one flood every five to six years. In the summer of 1931, breaches occurred at multiple places along both banks of Jingjiang, affecting 50.9 million acres of farmland and impacting a population of up to 28 million people.
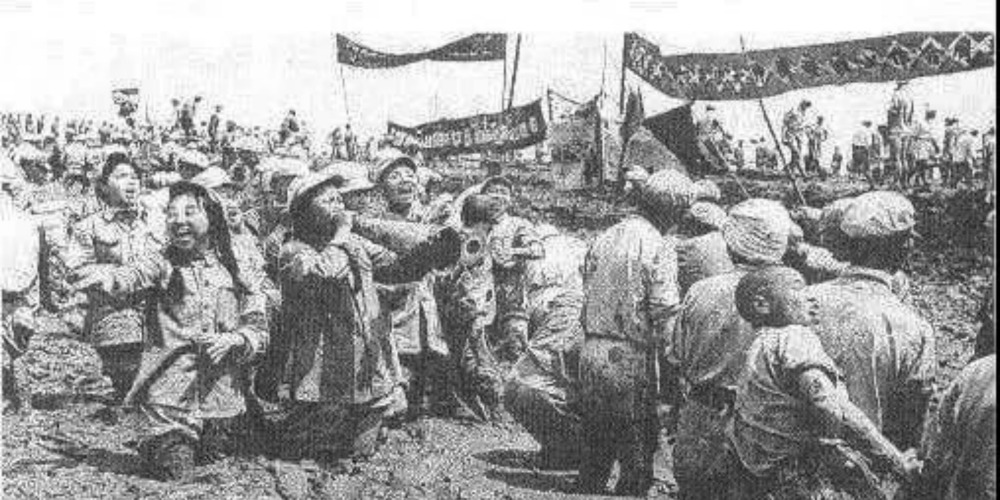
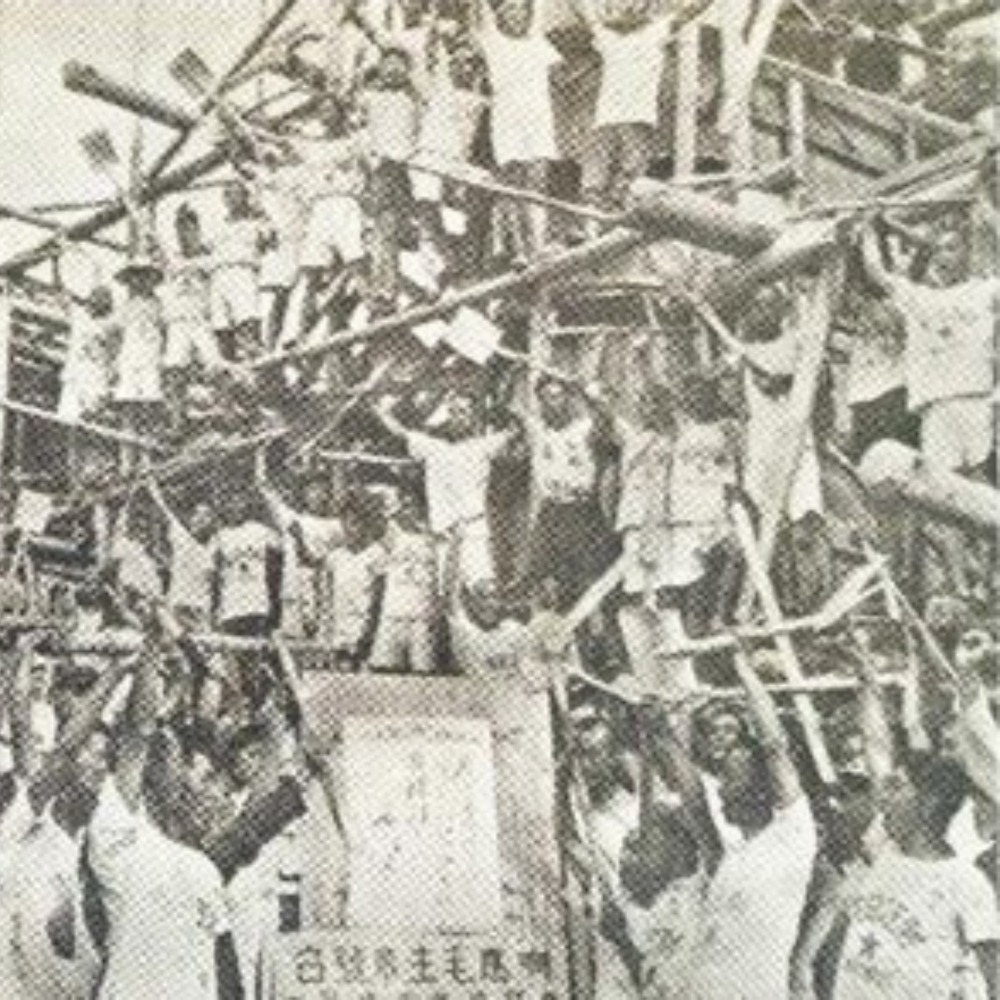
In the spring of 1952, the Chinese government mobilised more than 300,000 military and civilian personnel to participate in the construction of the Jingjiang flood diversion project.
The over 300,000 people completed the main body of the first phase of the project in just 75 days, by June 20.