Published : 2025-04-15
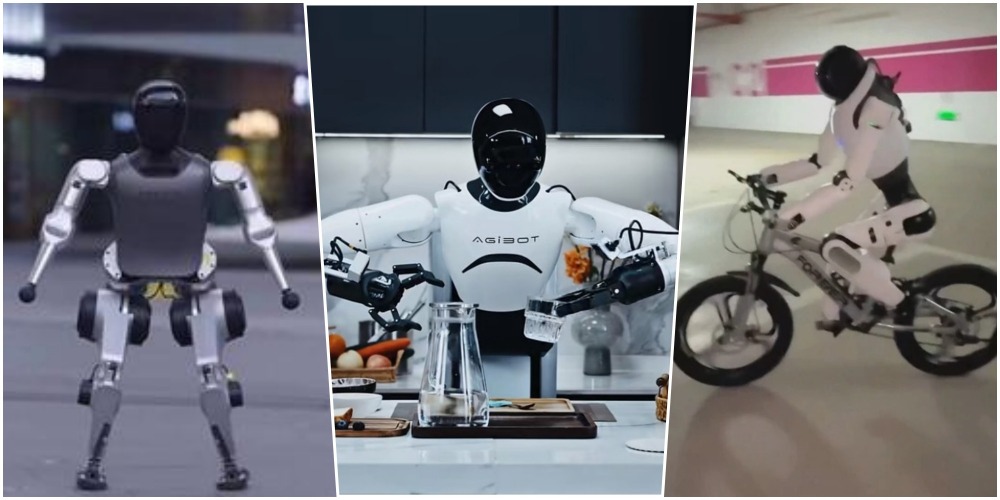
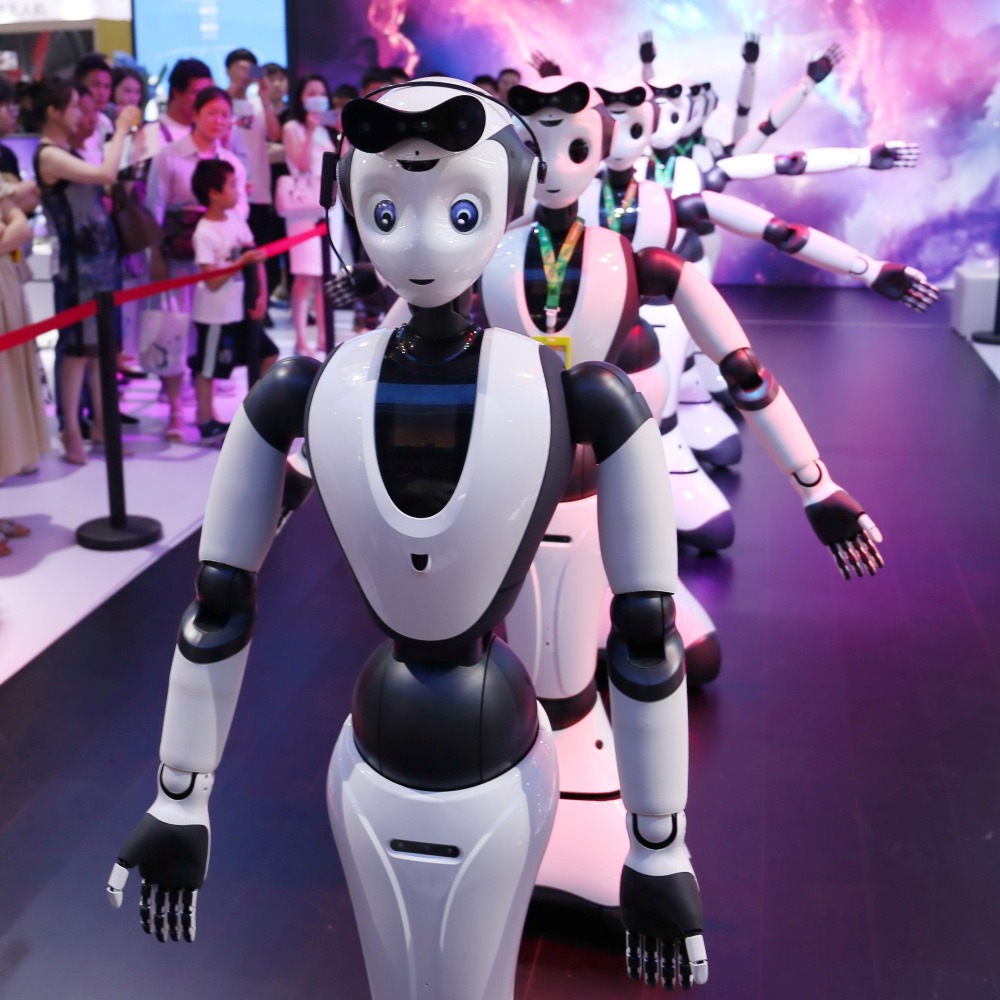
China's humanoid robots are rapidly "evolving."
After performing the traditional "Yangge Dance" on the Spring Festival Gala, domestically developed robots have mastered an ever-expanding repertoire of new skills, such as backflipping, bike-riding, and working in factories.
Let's take a look at what new skills the Chinese robots have learned and the technologies behind them.

Unitree and NOETIX create world's first side-flip and back-flip robots
Robots from Unitree Robotics (宇樹科技) have been making rapid progress. After performing the Yangge Dance at the Spring Festival Gala, they learned to walk on a balance beam and navigate "meihua zhuang" (a series of wooden stakes used in martial arts training) in less than a month.
On March 19, the Unitree G1 robot even successfully challenged standing side flip, becoming the first robot in the world to complete a side flip.
Read more: Can robots also perform the Yangko Dance and spin handkerchiefs?
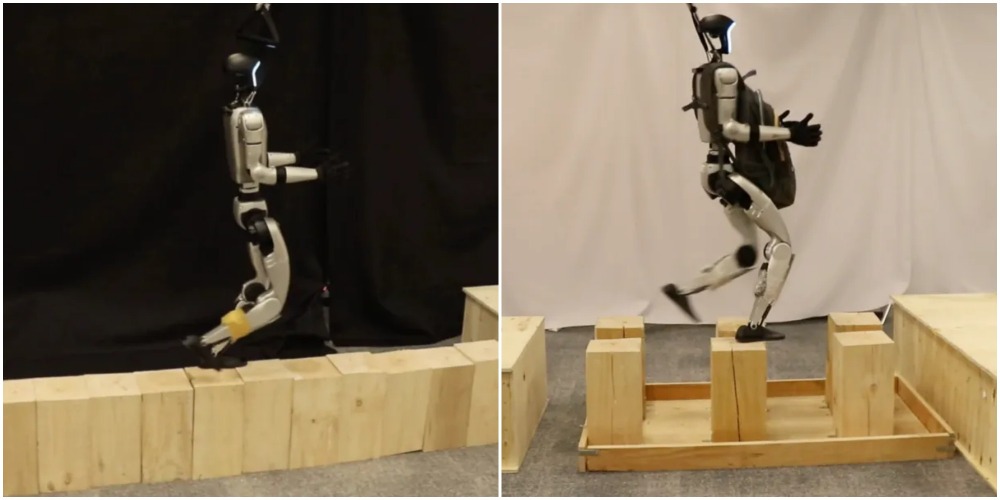
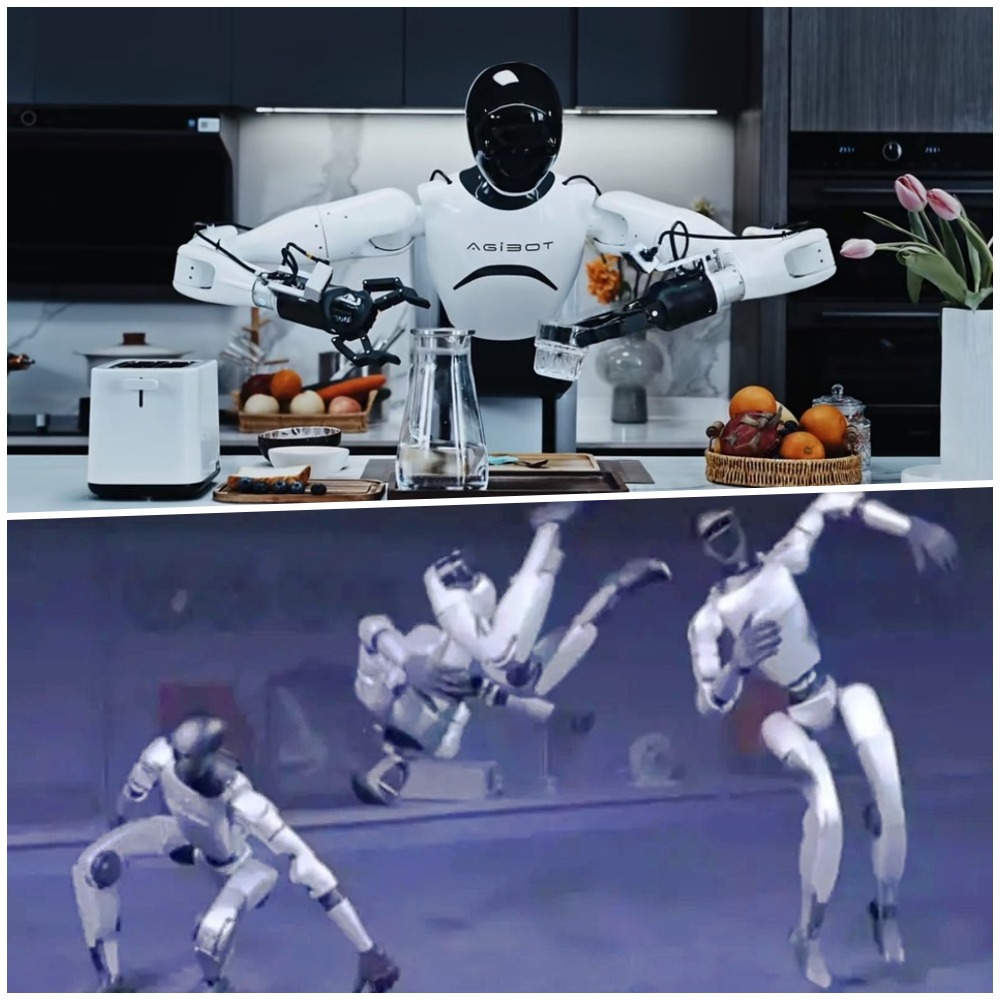
At the same time, the N2 robot from NOETIX (松延動力) has become the world's first robot to perform continuous backflips.
It can also perform precise actions such as single-leg hops, walking, and running easily. Although the backflip is a highly challenging action, the NOETIX team managed to teach the robot this skill in just three weeks, thanks to the support of artificial intelligence algorithms.
The team designed a "reinforcement learning" method that allows the robot to learn in a unexplored environment.
Like humans, it grows through continuous trial and error. The robot improves itself based on set standards, using "trial and error" and "punishment" to progress from simple to complex tasks. In this way it can find the most effective method to improve in the minimal time.
Read more: AI reporter and robotic dog drawing attention in China's Two Sessions
Proficient in cycling, sewing, and pouring water, AgiBot combine movement and interaction
The intelligent interactive humanoid robot "Lingxi X2" (靈犀X2) released by AgiBot (智元机器人) integrates three main functions: movement, interaction, and operation.
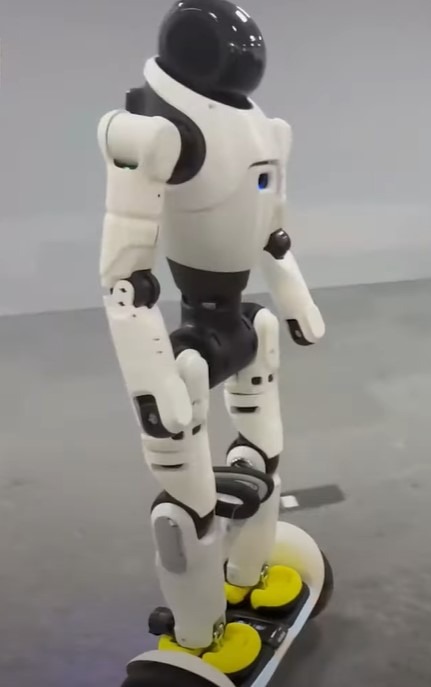
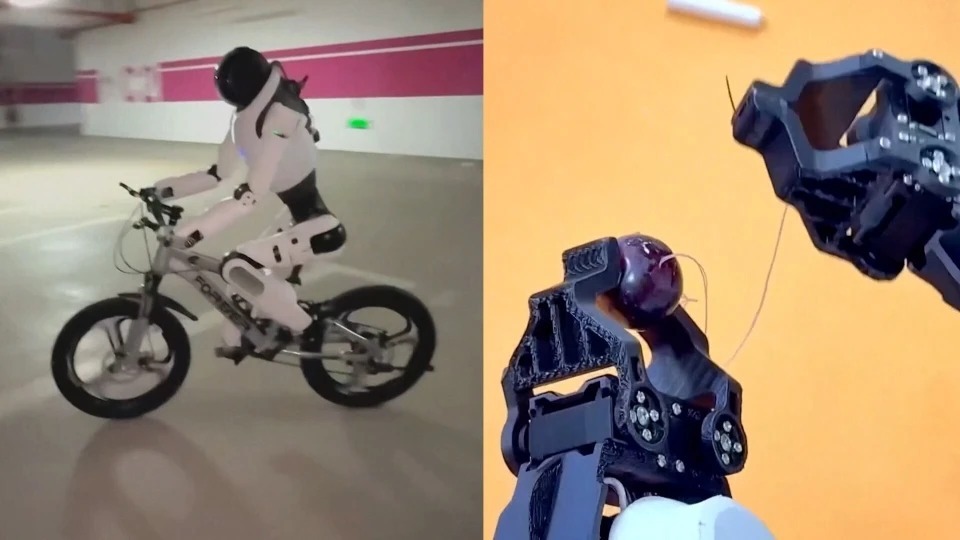
It has excellent balance and can ride bicycles, scooter and hoverboard. It also excels in intricate movements, capable of completing complex tasks such as grabbing, placing stuff and precise operation like sewing grapes.
Lingxi X2 not only has flexible and excellent movement capabilities but also has millisecond-level interactive response capabilities.
It is equipped with a multimodal interactive large language model "Gui Guang Dong Yu" (硅光動語), which allows it to capture emotional states by analysing human facial expressions and voice tones and then respond immediately. This interaction experience is natural and realistic, making human-machine communication closer.
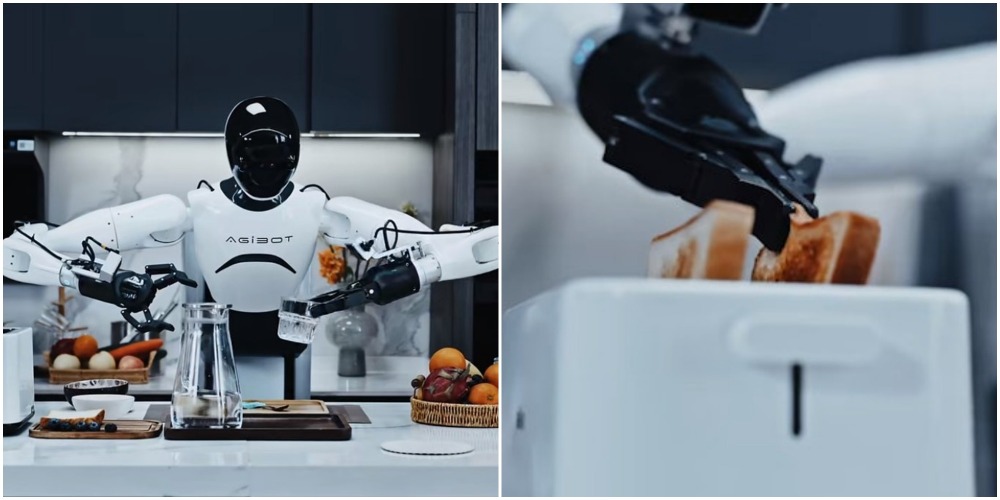
In March, AgiBot unveiled its first general-purpose embodied intelligence foundation model, Genie Operator-1 (GO-1). Unlike traditional models that require massive datasets for training, GO-1 achieves rapid skill acquisition with just hundreds of data samples, adapting efficiently to diverse tasks.
With the help of GO-1, the robot of AgiBot possess ground-breaking learning capabilities—it can master household tasks like pouring water and toasting bread simply by observing human demonstration videos.

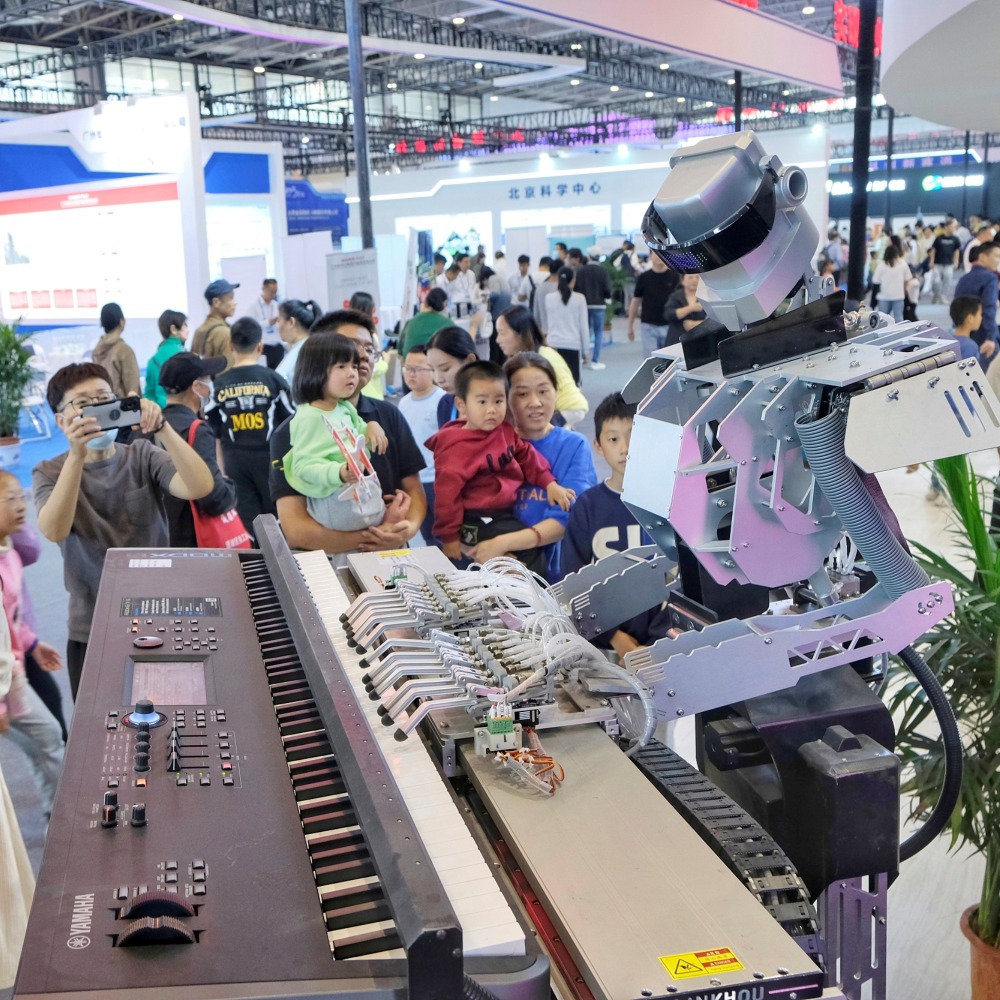
Embodied AI Robots start working in factories
Embodied intelligent robot start-up AI2Robotics (智平方科技) and Jingneng Microelectronics have officially cooperated to jointly develop an embodied robot solution for semiconductor factories, based on the embodied large model Alpha Brain and the Alpha Bot (愛寶). This marks the first application of embodied intelligence robots in advanced semiconductor factories.
Embodied intelligence is about integrating AI into physical "bodies" such as robots, giving them human-like abilities to perceive, learn, and interact with the environment like humans, as well as the capacity for thinking independently and using corresponding tools.

The Alpha Bots working in factories features 24 degrees of freedom and a single-arm payload capacity exceeding 5kg, achieving ±1mm high-precision positioning even in large-scale operations. They can execute precise grabbing and handling tasks around the clock and gradually achieve operations such as wafer loading and consumable replacement.
After entering the factories, the Alpha Bots will continue long-term learning, accumulating operational data to validate and refine its models – thereby developing autonomous, self-evolutionary capabilities for ongoing iteration.